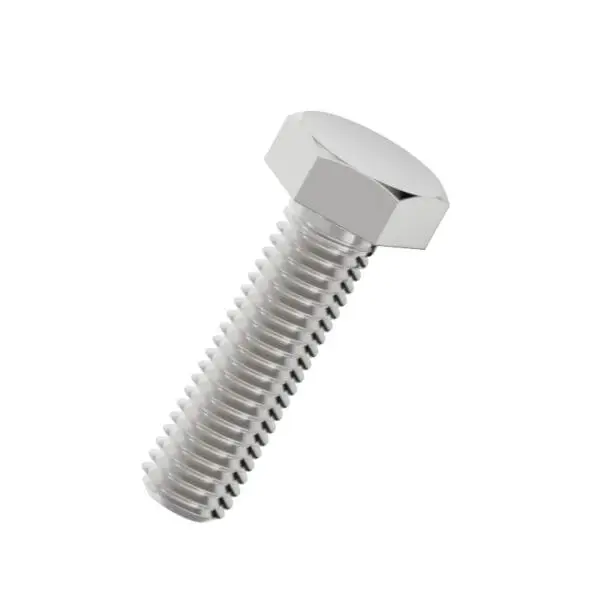
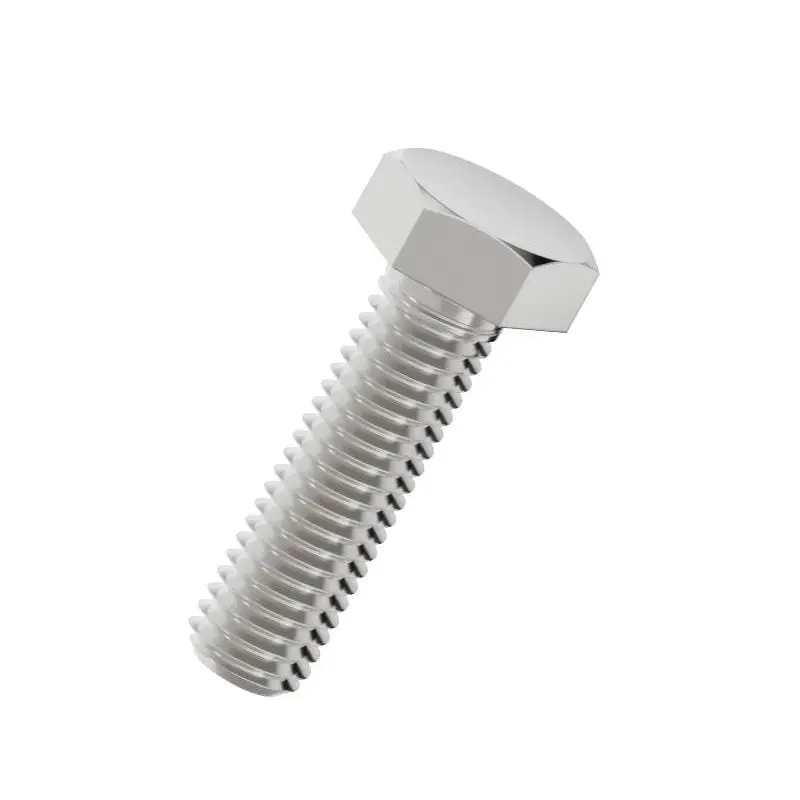
Stainless steel - Hexagon bolt
Precision Stainless Steel Hexagon Head Fasteners
Stainless steel hexagon bolts are essential structural components designed for high-integrity fastening applications. Featuring a six-sided head profile, these bolts are engineered to be driven by a wrench or socket, facilitating high torque application. Our selection is manufactured from corrosion-resistant austenitic steel, ensuring long-term durability and stability in various environmental conditions.
- Material Quality: Produced from premium Grade A2 (304) and A4 (316) stainless steel for superior rust and oxidation resistance.
- Head Geometry: Precision-forged hexagonal heads ensure secure wrench grip and prevent slippage during installation.
- Flexible Supply: We provide both single-box retail options and competitive wholesale pricing for bulk volume orders.

Technical Characteristics of Stainless Hex Bolts
Hexagon bolts represent the industry standard for securing heavy machinery and structural components. The external hex drive allows for significant leverage, making them suitable for applications requiring substantial clamping force. When manufactured from stainless steel, these bolts offer a vital combination of mechanical strength and resistance to environmental degradation, eliminating the need for protective coatings that can flake or wear off.Material Specifications and Properties
Choosing the right stainless steel grade is critical for ensuring the bolt can withstand both the physical load and the chemical environment. Our hex bolts are typically supplied in the cold-worked condition (Class 70) to ensure optimal tensile strength.| Steel Grade | AISI Standard | Performance in Hex Bolts | Tensile Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | 304 | Excellent for general atmospheric exposure. The standard choice for indoor and outdoor machinery where saltwater is not present. | Min. 700 N/mm² |
| A4 | 316 | Required for marine and chemical environments. The molybdenum content prevents pitting corrosion on the bolt head and shank. | Min. 700 N/mm² |
Quality Assurance and MTC
At Fastener Core, we prioritize transparency in material quality. We provide EN 10204 3.1 Material Test Certificates (MTC) free of charge upon request. These certificates validate the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the bolts supplied. While MTCs are complimentary, please note that any requests for third-party inspection services are subject to additional fees.Key Industrial Applications
Stainless steel hex bolts are widely utilized across industries that demand hygiene and longevity:- Water & Waste Management: Pump assembly and pipe flanges requiring resistance to moisture.
- Chemical Processing: Fastening tanks and vessels where chemical spill resistance is necessary.
- Food Industry: Conveyor systems and machinery where non-toxic, easy-to-clean fasteners are mandatory.
- Construction: Structural connections in outdoor architectural projects.