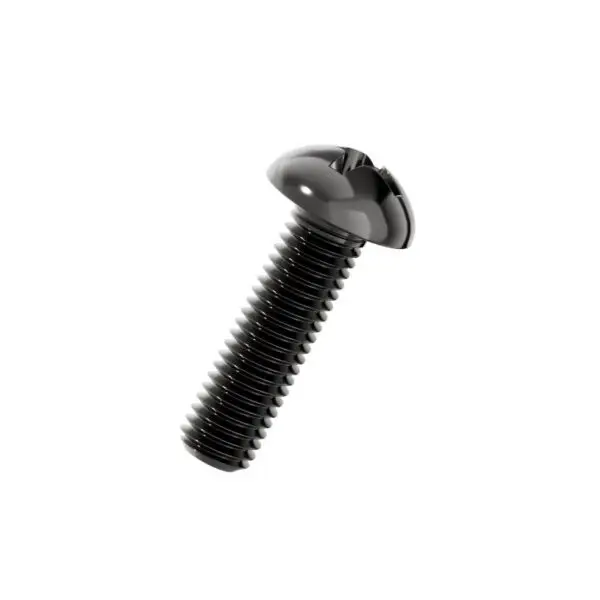
Cross recess pan head screw
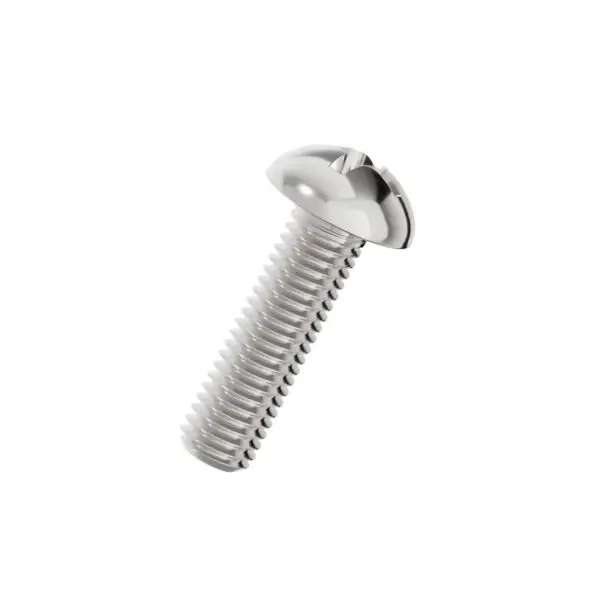
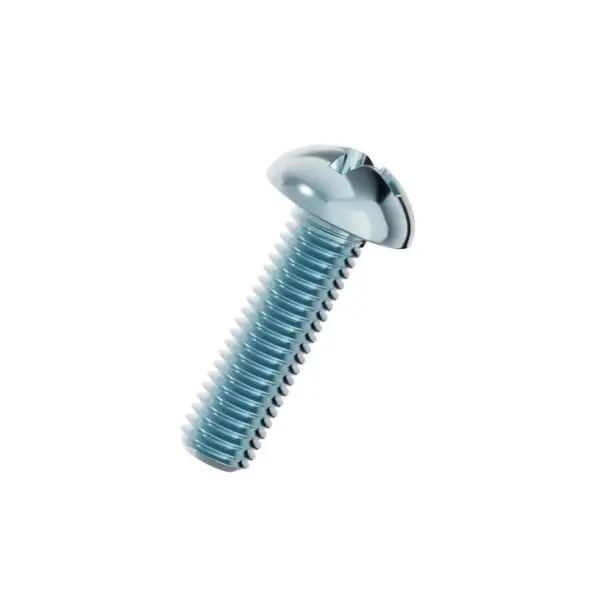
Cross Recess Pan Head Screws are among the most versatile and widely used fasteners in modern manufacturing. Featuring a rounded, low-profile head with a cruciform (Phillips) drive, these screws are designed for efficient assembly using manual or powered screwdrivers. The pan head provides a wide bearing surface that distributes clamping force without damaging the workpiece, making them ideal for securing sheet metal, plastic housings, and electronic components.
- Self-Centering Drive: The cross recess design allows the screwdriver bit to automatically align with the screw, speeding up assembly lines and reducing operator fatigue.
- Versatile Head Profile: The pan head offers a balance between low profile and high clamping area, suitable for a wide range of materials and thicknesses.
- Multiple Material Options: Available in Carbon Steel (Grades 4.8 and 8.8) with zinc plating, and corrosion-resistant Stainless Steel for demanding environments.
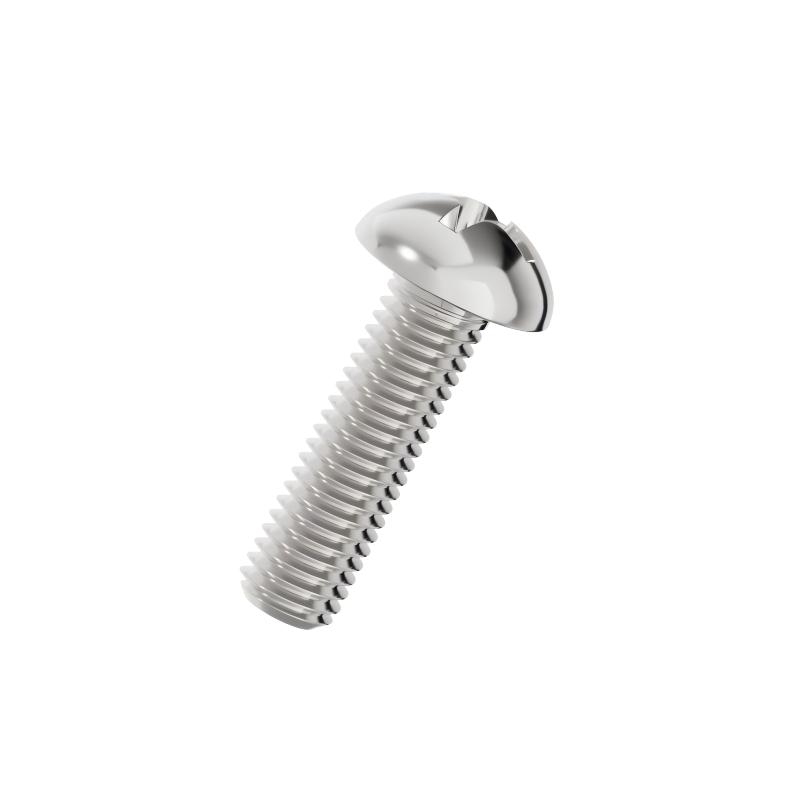

Understanding the Pan Head Geometry
The "Pan Head" is characterized by a slightlydomed top with a flat bearing surface underneath. It is taller than a countersunk head but lower than a round head, offering a practical compromise. This shape is designed to sit on top of the material (not flush), providing a visible but unobtrusive fastening point. The wide head diameter prevents the screw from pulling through thin sheet materials.The Cross Recess (Phillips) Drive
The cross recess, commonly known as the Phillips drive, is engineered for high-speed automated assembly. Unlike a slotted screw, the cruciform shape allows the driver bit to engage quickly without needing precise alignment. Additionally, the Phillips design has a built-in "cam-out" feature—when torque exceeds a certain level, the bit will slip out of the recess, reducing the risk of over-tightening and stripping the screw head.Material and Finish Options
We offer cross recess pan head screws in several material and surface treatment combinations to suit your application:- Grade 4.8 Carbon Steel (White Zinc)
- The standard choice for general-purpose fastening. Offers adequate strength for light-duty applications with a bright, corrosion-resistant finish suitable for indoor use.
- Grade 4.8 Carbon Steel (Black Zinc)
- Provides the same mechanical properties as white zinc but with a darker aesthetic. Often preferred for electronics and equipment where a non-reflective finish is desired.
- Grade 8.8 Carbon Steel (White Zinc)
- A high-tensile option for applications requiring greater clamping force. Suitable for automotive and machinery where vibration resistance is important.
- Stainless Steel (A2/A4)
- The premium choice for outdoor, marine, or food-grade applications. Offers inherent corrosion resistance without relying on a plated coating.
Quality Assurance
We ensure consistent quality across all material grades. An EN 10204 3.1 Material Certificate is available upon request to verify the chemical composition of your batch. Please note that third-party inspection services require an additional fee.Common Applications
Cross recess pan head screws are ubiquitous in modern industry:- Consumer Electronics: Securing plastic housings on TVs, computers, and appliances.
- Electrical Panels: Fastening terminal covers and junction boxes.
- Automotive Interiors: Attaching trim panels and dashboard components.
- HVAC Systems: Assembling ductwork and ventilation covers.