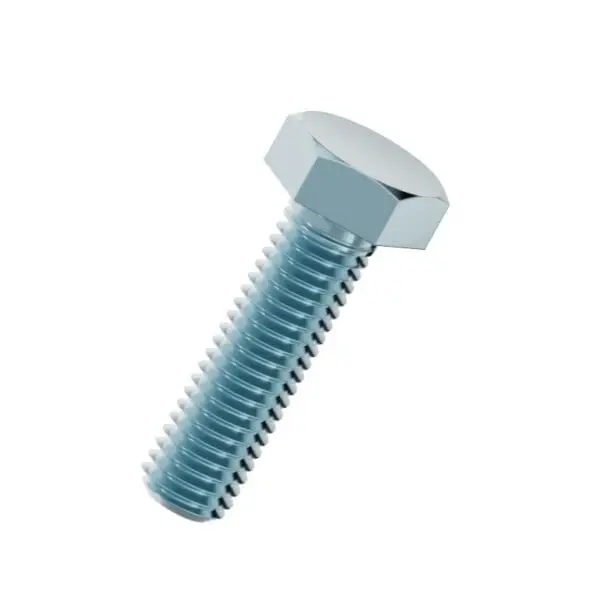
White zinc - Hexagon bolt
Zinc Plated Steel Hexagon Bolts (Grades 4.8 - 12.9)
Our white zinc hexagon bolts provide a versatile fastening solution that balances structural strength with cost-effective corrosion protection. Manufactured from carbon and alloy steels, these bolts undergo an electro-galvanizing process to create a smooth, bright silver-white finish. This coating acts as a barrier against moisture, making them ideal for indoor industrial equipment, automotive assembly, and general construction.
- Comprehensive Grading: Stocked in a full range of strength classes: 4.8 (Low Carbon), 8.8 (High Tensile), and 10.9/12.9 (High Strength Alloy).
- Surface Finish: The white zinc plating offers a clean, aesthetic appearance while protecting the underlying steel from oxidation in dry and non-aggressive environments.
- Wholesale Solutions: We support diverse procurement strategies, offering volume discounts for full pallet orders alongside flexible options for smaller maintenance requirements.

Overview of White Zinc Hex Bolts
White zinc hexagon bolts are the standard choice for the vast majority of industrial and commercial fastening applications where stainless steel is not required. The "White Zinc" finish is achieved through electro-plating zinc onto the steel, followed by a clear or blueish chromate conversion coating. This process not only delays corrosion but also provides a lubricant effect that assists in installation. The hexagonal head is designed to handle high torque transmission, making these bolts ideal for structural assembly.Property Classes and Material Specifications
Selecting the correct strength grade is vital for safety. A bolt usually fails due to improper grade selection rather than manufacturing defects. We offer the following grades in white zinc plating:| Grade | Material Type | Typical Application | Tensile Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.8 | Low Carbon Steel (Mild) | Non-critical fastening, furniture, fencing, and light maintenance where shear loads are low. | 400 N/mm² |
| 8.8 | Medium Carbon Steel (Quenched & Tempered) | The industrial standard for "High Tensile" bolts. Used in structural steelwork, automotive engines, and heavy machinery. | 800 N/mm² |
| 10.9 | Low Carbon Alloy Steel (Quenched & Tempered) | High-stress applications requiring superior strength-to-weight ratios, such as automotive suspension parts. | 1000 N/mm² |
| 12.9 | Alloy Steel (Quenched & Tempered) | Critical clamping applications like hydraulic clamping and heavy forging machinery. | 1200 N/mm² |
Quality Control and Certificates
Ensuring the steel grade matches the stamp on the head is our priority. Fastener Core provides EN 10204 3.1 Material Test Certificates (MTC) free of charge upon request. Please note that while MTCs are complimentary, third-party verification services are available at an additional cost.Common Industrial Uses
White zinc plated hex bolts are versatile and found in numerous sectors:- Automotive & Transport: Grade 8.8 and 10.9 bolts are extensively used for chassis and engine components.
- Warehousing: Assembly of racking and shelving units (typically Grade 4.8 or 8.8).
- General Machinery: Fastening motors, guards, and casings in indoor factories.
- Consumer Goods: Furniture assembly and DIY hardware due to the clean appearance of the zinc finish.