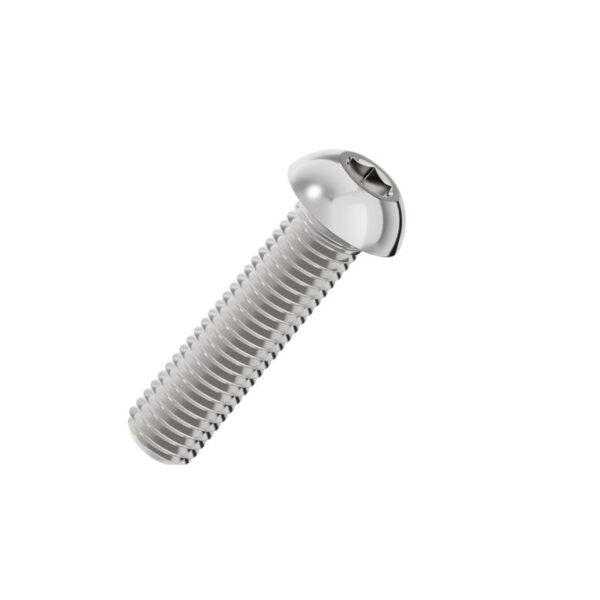
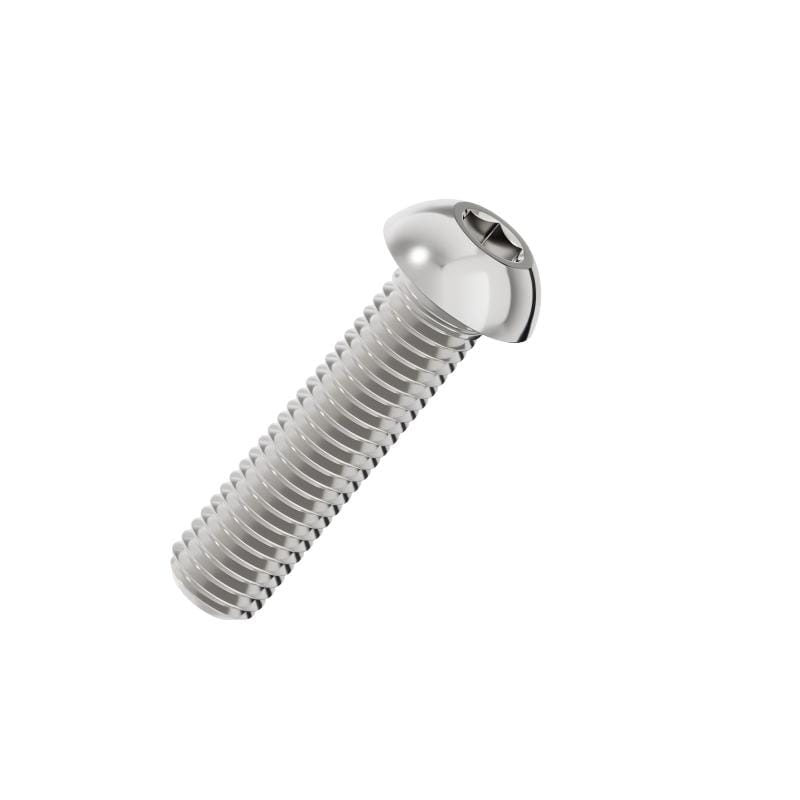
Hexagon socket button head screw
Hexagon Socket Button Head Screws are characterized by their rounded, dome-shaped head and low profile. Designed to meet ISO 7380 standards, these fasteners offer a streamlined appearance and a safety-conscious design that lacks sharp edges, making them ideal for external applications where snagging must be avoided. Driven by an internal hexagonal socket, they provide controlled torque application in areas where space is limited, serving as a functional yet aesthetic solution for modern assembly.
- Safety Design: The smooth, rounded head eliminates sharp corners, reducing the risk of injury or snagging on clothing and equipment.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The low-profile dome shape sits closer to the surface than a standard cap screw, providing a clean, finished look for visible assemblies.
- Supply Consistency: We maintain a vast inventory of standard metric sizes, supporting both rapid prototyping orders and large-scale wholesale production.

Understanding the Button Head Geometry
The Hexagon Socket Button Head Screw is distinct from the standard Socket Cap Screw (DIN 912) due to its head geometry. The "Button" head is wider and flatter. This design is primarily chosen for two reasons: clearance and cosmetics. When vertical space is restricted, or when a fastener is exposed on the outside of a machine guard or panel, the button head offers a sleek solution that blends into the surface profile better than taller fasteners.Mechanical Load Limitations
Reduced Loadability (ISO 7380): It is critical for engineers to understand that button head screws are generally not designed for high-strength structural applications in the same way as cylindrical cap screws. Due to the reduced head height and smaller internal hex drive size, they cannot withstand the same high torque values or tensile loads as a DIN 912 screw of the same diameter. Application Guidance: Regardless of the material (whether steel or stainless), button head screws are typically intended for holding covers, panels, brackets, and guards where the primary forces are shear or light tension. They should be used with caution in critical high-stress joints where bolt stretch is required.Quality Assurance
At Fastener Core, precision is our standard. We can provide an EN 10204 3.1 Material Certificate upon request to verify the dimensional compliance and material composition of your order. Please note that third-party inspection services are available for an additional fee.Common Industrial Applications
Due to their smooth finish and low profile, these screws are widely used in:- Automotive Styling: Body kits, interior panels, and engine bay aesthetics.
- Public Furniture: Park benches and bus stops where sharp edges could cause injury to the public.
- Electronics: Computer cases and server racks where internal clearance is tight.
- Machinery Guards: Fastening protective covers where a snag-free surface is a safety requirement.